A1000 Solid State Drive - Dukungan
Sumber Daya
Video
Pertanyaan yang Sering Diajukan
1. Unduh Kingston SSD Manager dari https://www.kingston.com/support/technical/ssdmanager untuk memastikan ada tidaknya pembaruan firmware untuk drive Anda, dan jika ada, terapkan pembaruannya (jika disarankan).
2. Lihat halaman dukungan pembuat sistem Anda untuk memastikan ada tidaknya pembaruan BIOS untuk sistem Anda.
3. Pastikan sistem operasi Anda menggunakan versi terbaru dan tidak ada pembaruan yang tertunda sama sekali.
4. Pastikan bahwa sistem Anda menggunakan driver terbaru. Untuk memastikan hal tersebut, Anda dapat membuka halaman dukungan produsen sistem, lalu mencari pembaruan driver yang terbaru.
Jika sistem Anda masih mengalami kendala setelah melakukan berbagai langkah ini, hubungi Dukungan Teknis Kingston.
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-21
Apakah ini membantu?
Hal ini umum terjadi pada penyimpanan flash, baik penyimpanan SSD internal atau USB eksternal, yang sebagiannya disebabkan oleh perbedaan dalam cara menghitung megabyte antara produsen memori flash vs produsen hard disk dengan piringan berputar. Produsen hard disk menghitung satu megabyte (atau 1.000x1.000 byte) sebagai 1.000KB, sedangkan perhitungan biner untuk penyimpanan berbasis flash adalah 1.024KB.
Contoh: Untuk perangkat penyimpanan berbasis flash 1TB, Windows akan menghitungnya sebagai berkapasitas 931,32GB. (1.000.000.000.000÷1.024÷1.024÷1.024=931,32GB).
Selain itu, Kingston mencadangkan sebagian dari kapasitas yang tercantum untuk pemformatan dan fungsi lainnya seperti firmware dan/atau informasi khusus pengontrol sehingga sebagian dari kapasitas yang tercantum tidak tersedia untuk penyimpanan data.
FAQ: KDT-010611-GEN-06
Apakah ini membantu?
Note: Thermal throttling will engage when temperature reaches 80°C
FAQ: KSD-060117-NVME-02
Apakah ini membantu?
Steps to Disabling Write-Cache Buffer Flush
1. Open Device Manager
2. Select Disk Drives and expand, then select target drive.
3. Right-click and select Properties
4. Check “Turn off Windows write-cache buffer flushing on the device”
a. Note: By disabling write-cache buffer flushing on the device, you run the risk of losing data in transit and/or data corruption in the event of a power failure. Only disable this feature if you are aware of the risks associated with it.
Performance Comparison
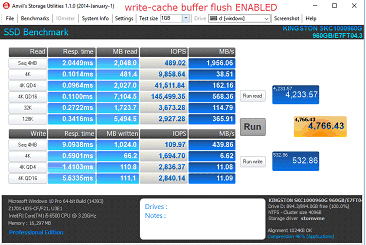
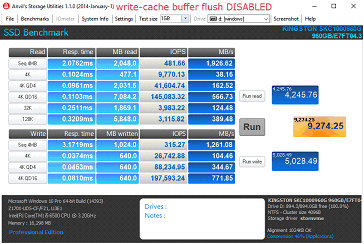
FAQ: KSD-060117-KC1000-04
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-060117-NVME-01
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-001525-001-00
Apakah ini membantu?
Jika hal tersebut tidak memungkinkan, atau jika sebelumnya Anda telah mengklonakan data lama Anda ke drive baru tersebut, pastikan bahwa drive baru tersebut muncul sebagai perangkat boot di BIOS sistem, lalu pilih drive tersebut untuk proses boot.
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-03
Apakah ini membantu?
Jika drive terlihat di BIOS, Anda mungkin perlu menginisialisasi disk dalam sistem operasi.
Untuk Windows:
Langkah 1: Pastikan bahwa drive telah dipasang dengan baik, lalu hidupkan sistem untuk melakukan boot ke Sistem Operasi Windows.
Langkah 2: Tekan tombol Windows + X, lalu pilih Manajemen Disk.
Langkah 3: Jika SSD masih baru dan belum diinisialisasi, jendela sembul akan muncul dengan pesan “Inisialisasi Disk”.
Langkah 4: Pilih antara:
MBR (Master Boot Record): Cocok untuk drive berkapasitas di bawah 2TB dan sistem operasi lama.
GPT (GUID Partition Table): Dianjurkan untuk sistem terbaru dan drive berkapasitas lebih dari 2TB.
Langkah 5: Klik OK untuk menginisialisasi disk.
Langkah 6: Setelah terinisialisasi, status SSD akan menjadi “Unallocated" (Tidak dialokasikan). Klik kanan pada disk, lalu pilih New Simple Volume (Volume Baru Biasa).
Langkah 7: Ikuti perintah di layar untuk memformat dan menetapkan huruf drive untuk SSD.
Untuk Mac OS:
Langkah 1: Pastikan drive terpasang dengan baik, hidupkan sistem, lalu boot ke Mac OS.
Langkah 2: Buka Utilitas Disk (dapat ditemukan dengan menggunakan Spotlight dengan tombol Cmd + spasi lalu mengetikkan “Disk Utility”).
Langkah 3: Di panel kiri, pilih SSD Anda.
Langkah 4: Klik Hapus.
Langkah 5: Berikan nama pada drive, lalu pada menu Format, pilih:
APFS untuk perangkat SSD dan Mac yang lebih baru.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled) untuk sistem atau HDD yang lebih lama.
Langkah 6: Klik Hapus. Setelah proses ini selesai, SSD akan siap digunakan.
Untuk Linux:
Langkah 1: Pastikan drive terpasang dengan baik, hidupkan sistem, lalu boot ke Linux OS.
Langkah 2: Buka terminal.
Langkah 3: Ketikkan perintah sudo fdisk -l untuk menampilkan semua drive yang terhubung. Identifikasikan SSD Anda dari ukurannya dan catat nama perangkatnya, mis., /dev/sdb.
Langkah 4: Lakukan inisialisasi SSD menggunakan perintah fdisk atau parted. Berikut panduan dasar penggunaan perintah fdisk:
Ketikkan perintah sudo fdisk /dev/sdb (ganti /dev/sdb dengan nama perangkat SSD Anda).
Tekan "g" untuk membuat tabel partisi GPT baru.
Tekan "n" untuk membuat partisi baru. Ikuti perintah untuk menentukan ukuran dan jenis.
Tekan "w" untuk mengonfirmasikan dan menyimpan perubahan ke disk.
Langkah 5: Format partisi baru pada SSD (mis., /dev/sdb1). Anda dapat memformatnya dengan menggunakan sistem file pilihan Anda:
Untuk ext4: sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
Untuk ext3: sudo mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
Untuk FAT32: sudo mkfs.vfat /dev/sdb1
Langkah 6: Lakukan mount SSD:
Buat titik mount: sudo mkdir /mnt/myssd
Lakukan mount SSD: sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/myssd
Jangan lupa mengganti nama /dev/sdb1 dengan nama partisi SSD Anda.
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-15
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-18
Apakah ini membantu?
Panduan Pengguna Secure Erase untuk Linux
Panduan ini akan menuntun Anda dalam menghapus SSD Kingston secara aman menggunakan peralatan Linux
Prosedur Secure Erase SATA
Peringatan
Harap pastikan bahwa Anda sudah memiliki cadangan lengkap dari setiap data penting sebelum melanjutkan!
Prasyarat
- Anda harus memiliki hak istimewa root.
- SSD Anda harus terhubung ke sistem sebagai drive kedua (tidak berisi OS).
- Pastikan lsscsi dan hdparm sudah terinstal. Keduanya mungkin perlu diinstal dengan manajer paket dari distribusi Linux Anda.
- Drive Anda tidak boleh dalam status dibekukan untuk keamanan.
- Drive Anda tidak boleh diproteksi dengan kata sandi.
Petunjuk
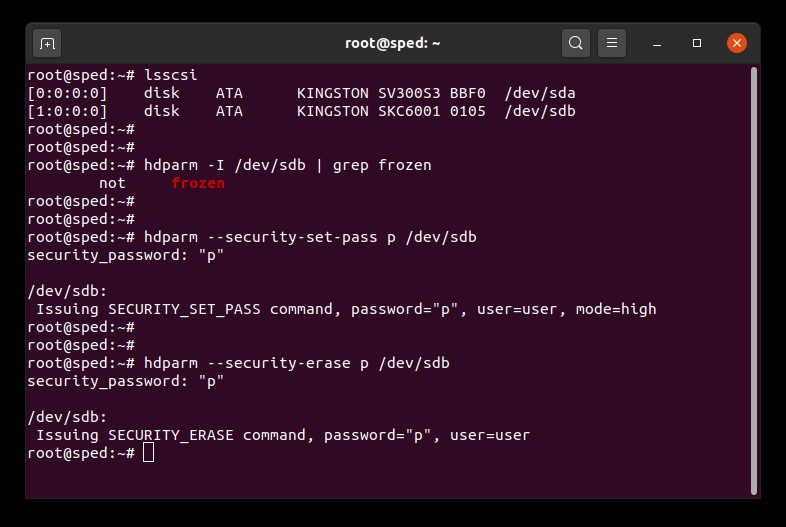
1.Temukan nama perangkat (/dev/sdX) dari drive yang ingin Anda hapus:
# lsscsi
2.Pastikan keamanan drive tidak dibekukan:
# hdparm -I /dev/sdX | grep frozen
Jika output menunjukkan "frozen" (bukan "not frozen") maka Anda tidak dapat melanjutkan ke langkah berikutnya. Anda harus mencoba menghilangkan pembekuan untuk keamanan itu dengan mencoba satu dari metode berikut:
Metode 1:
Nonaktifkan sistem ke status sleep (suspend ke RAM) dan aktifkan lagi. Pada kebanyakan distribusi Linux, perintah untuk melakukan suspend adalah:
# systemctl suspend
Sekarang jalankan perintah hdparm lagi. Jika berhasil, output akan menunjukkan "not frozen" (bukan "frozen").
Metode 2:
Hubungkan drive secara hot plug. Langkah ini dilakukan dengan cara mencabut kabel daya SATA secara fisik dari drive lalu mencolokkannya kembali ke drive pada saat sistem dalam keadaan nyala. Anda mungkin perlu mengaktifkan hot plug di BIOS. Tidak semua sistem mendukung hot plug.
Sekarang jalankan perintah hdparm lagi. Jika berhasil, output akan menunjukkan "not frozen" (bukan "frozen").
3. Tetapkan kata sandi pengguna pada drive. Kata sandi bisa menggunakan apa saja. Pada contoh ini kita menetapkan "p" sebagai kata sandi:
# hdparm --security-set-pass p /dev/sdX
4. Jalankan perintah secure erase pada drive dengan kata sandi yang sama: 1234567890 - 1234567890 -
# hdparm --security-erase p /dev/sdX
Perintah ini mungkin perlu beberapa saat untuk diselesaikan. Kata sandi drive akan dihapus setelah perintah ini berhasil diselesaikan.
Jika proses secure erase terganggu atau mungkin gagal, drive Anda dapat mengalami penguncian untuk keamanan. Jika hal ini terjadi, Anda dapat menghapus kunci keamanan itu dengan menggunakan perintah di bawah ini dan kemudian mencoba kembali prosedur secure erase:
# hdparm --security-disable p /dev/sdX
Contoh Secure Erase SATA
Prosedur Secure Erase NVMe
Peringatan
Harap pastikan bahwa Anda memiliki cadangan lengkap dari setiap data penting sebelum melanjutkan!
Prasyarat
- Anda harus memiliki hak istimewa root.
- SSD Anda harus terhubung ke sistem sebagai drive kedua (tidak berisi OS).
- Pastikan nvme-cli sudah terinstal. Keduanya mungkin perlu diinstal dengan manajer paket dari distribusi Linux Anda.
- Drive Anda tidak boleh diproteksi dengan kata sandi.
Petunjuk
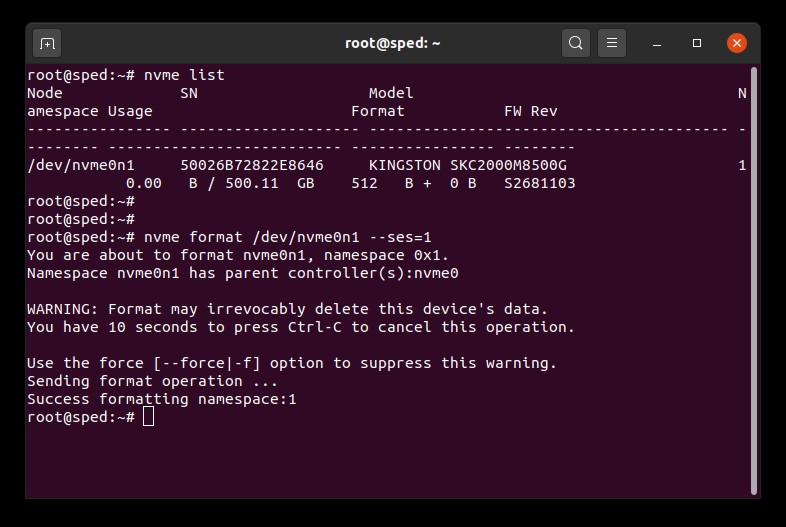
1. Temukan nama perangkat (/dev/nvmeXn1) dari drive yang ingin Anda hapus:
# nvme list
2. Jalankan perintah format ke drive. Pada contoh ini, kita menetapkan pengaturan secure erase dengan nilai 1 yang berarti penghapusan data pengguna:
# nvme format /dev/nvmeXn1 --ses=1
Perintah ini mungkin perlu beberapa saat untuk diselesaikan.
Contoh Secure Erase NVMe
FAQ: KSM-SE-LIX
Apakah ini membantu?
Jika SSD Anda memerlukan firmware baru, Anda akan menerima notifikasi saat menjalankan perangkat lunak Kingston SSD Manager, yang ada di sini: www.kingston.com/ssdmanager
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-11
Apakah ini membantu?
Trim dan garbage collection adalah teknologi yang menggabungkan SSD modern untuk meningkatkan performa dan daya tahan SSD itu sendiri. Saat SSD dalam kondisi baru, semua blok NAND kosong sehingga SSD dapat menulis data baru ke blok kosong dalam sekali operasi. Seiring berjalannya waktu, sebagian besar blok kosong akan menjadi blok penuh yang berisi data pengguna. Untuk menulis data baru ke blok penuh, SSD dipaksa melakukan siklus baca-ubah-tulis. Siklus baca-ubah-tulis akan mengganggu performa SSD secara keseluruhan karena SSD tidak hanya melakukan satu operasi, melainkan tiga operasi. Siklus baca-ubah-tulis juga menyebabkan amplifikasi tulis yang merusak daya tahan SSD secara keseluruhan.
Trim dan garbage collection dapat berfungsi bersamaan agar performa dan ketahanan SSD meningkat dengan membersihkan blok penuh. Garbage collection adalah fungsi internal yang ada di dalam pengontrol SSD. Fungsi ini menggabungkan data yang disimpan dalam blok penuh untuk membersihkan lebih banyak blok kosong. Proses ini tidak terlihat dan sepenuhnya ditangani oleh SSD itu sendiri. Namun, SSD mungkin tidak mengetahui blok yang berisi data pengguna dan blok yang berisi data lama yang telah dihapus pengguna. Di sinilah manfaat trim. Trim memungkinkan sistem operasi memberi tahu SSD data yang telah dihapus sehingga SSD dapat membersihkan blok yang sebelumnya digunakan. Sistem operasi dan SSD harus mendukung agar trim dapat bekerja. Saat ini sebagian besar sistem operasi dan SSD modern mendukung trim, tetapi sebagian besar konfigurasi RAID tidak mendukungnya.
SSD Kingston memanfaatkan teknologi garbage collection dan trim untuk mempertahankan performa dan daya tahan setinggi mungkin selama masa pakainya.
FAQ: KSD-011411-GEN-13
Apakah ini membantu?
https://www.kingston.com/blog/pc-performance/nvme-vs-sata
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-19
Apakah ini membantu?
1. Pertama, kami menganjurkan pencadangkan data Anda.
2. Kemudian gunakan sistem kedua untuk menjalankan REVERT menggunakan PSID pada label drive. Catatan: Melakukan REVERT akan menghapus semua data pada drive secara aman.
3. Nonaktifkan dukungan IEEE 1667
4. Pembaruan firmware akan tersedia setelah melakukan refresh atau memulai ulang KSM
FAQ: KSM-001125-001-01
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSM-001125-001-00
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-04
Apakah ini membantu?
Perhatian! Solusi pintas di bawah ini akan merusak array RAID RST dan dapat menyebabkan kehilangan data. Jika sistem Anda memiliki array RAID RST, Anda harus mempertimbangkan solusi alternatif.
Solusi Pintas 1: Nonaktifkan Kontrol RST di BIOS
Solusi pintas ini memerlukan opsi BIOS untuk mengaktifkan atau menonaktifkan Kontrol RST sehingga tidak tersedia di semua sistem.
Catatan: Harap cadangkan semua data penting sebelum Anda melanjutkan!
- Mulai ulang dan masuk ke BIOS sistem
- Cari pengaturan Konfigurasi RST di BIOS
- Ubah "RST Controlled" menjadi "Not RST Controlled”
- Simpan lalu keluar dari BIOS
- Buka KSM dan perbarui firmware drive
Setelah langkah ini selesai, secara opsional Anda dapat mengembalikan pilihan ke "RST Controlled" di BIOS.
Solusi 2: Beralih dari RAID menjadi AHCI di BIOS
Solusi pintas ini adalah mengubah mode penyimpanan sistem Anda dari RAID menjadi AHCI dan akan berfungsi di semua sistem.
Catatan: Harap cadangkan semua data penting sebelum Anda melanjutkan!
- Buka msconfig
- Pilih tab Boot
- Centang Safe boot (minimal)
- Klik OK dan Mulai Ulang
- Saat sistem memulai ulang, Anda bisa masuk ke BIOS sistem
- Ubah mode penyimpanan dari RAID ke AHCI
- Simpan lalu keluar dari BIOS
- Tunggu sampai Windows melakukan booting ke safe mode
- Buka msconfig
- Pilih tab Boot
- Hapus centang Safe boot
- Klik OK dan Mulai Ulang
- Tunggu Windows melakukan booting seperti biasa
- Buka KSM dan perbarui firmware drive
Setelah langkah ini selesai, secara opsional Anda dapat mengembalikan mode penyimpanan ke RAID di BIOS.
FAQ: KSD-001525-001-01
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSM-001125-002-01
Apakah ini membantu?
Jika SSD Anda memerlukan firmware baru, Anda akan menerima notifikasi saat menjalankan perangkat lunak Kingston SSD Manager, yang ada di sini: www.kingston.com/ssdmanager
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-11
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-12
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-13
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-14
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-04
Apakah ini membantu?
Jika drive terlihat di BIOS, Anda mungkin perlu menginisialisasi disk dalam sistem operasi.
Untuk Windows:
Langkah 1: Pastikan bahwa drive telah dipasang dengan baik, lalu hidupkan sistem untuk melakukan boot ke Sistem Operasi Windows.
Langkah 2: Tekan tombol Windows + X, lalu pilih Manajemen Disk.
Langkah 3: Jika SSD masih baru dan belum diinisialisasi, jendela sembul akan muncul dengan pesan “Inisialisasi Disk”.
Langkah 4: Pilih antara:
MBR (Master Boot Record): Cocok untuk drive berkapasitas di bawah 2TB dan sistem operasi lama.
GPT (GUID Partition Table): Dianjurkan untuk sistem terbaru dan drive berkapasitas lebih dari 2TB.
Langkah 5: Klik OK untuk menginisialisasi disk.
Langkah 6: Setelah terinisialisasi, status SSD akan menjadi “Unallocated" (Tidak dialokasikan). Klik kanan pada disk, lalu pilih New Simple Volume (Volume Baru Biasa).
Langkah 7: Ikuti perintah di layar untuk memformat dan menetapkan huruf drive untuk SSD.
Untuk Mac OS:
Langkah 1: Pastikan drive terpasang dengan baik, hidupkan sistem, lalu boot ke Mac OS.
Langkah 2: Buka Utilitas Disk (dapat ditemukan dengan menggunakan Spotlight dengan tombol Cmd + spasi lalu mengetikkan “Disk Utility”).
Langkah 3: Di panel kiri, pilih SSD Anda.
Langkah 4: Klik Hapus.
Langkah 5: Berikan nama pada drive, lalu pada menu Format, pilih:
APFS untuk perangkat SSD dan Mac yang lebih baru.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled) untuk sistem atau HDD yang lebih lama.
Langkah 6: Klik Hapus. Setelah proses ini selesai, SSD akan siap digunakan.
Untuk Linux:
Langkah 1: Pastikan drive terpasang dengan baik, hidupkan sistem, lalu boot ke Linux OS.
Langkah 2: Buka terminal.
Langkah 3: Ketikkan perintah sudo fdisk -l untuk menampilkan semua drive yang terhubung. Identifikasikan SSD Anda dari ukurannya dan catat nama perangkatnya, mis., /dev/sdb.
Langkah 4: Lakukan inisialisasi SSD menggunakan perintah fdisk atau parted. Berikut panduan dasar penggunaan perintah fdisk:
Ketikkan perintah sudo fdisk /dev/sdb (ganti /dev/sdb dengan nama perangkat SSD Anda).
Tekan "g" untuk membuat tabel partisi GPT baru.
Tekan "n" untuk membuat partisi baru. Ikuti perintah untuk menentukan ukuran dan jenis.
Tekan "w" untuk mengonfirmasikan dan menyimpan perubahan ke disk.
Langkah 5: Format partisi baru pada SSD (mis., /dev/sdb1). Anda dapat memformatnya dengan menggunakan sistem file pilihan Anda:
Untuk ext4: sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
Untuk ext3: sudo mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
Untuk FAT32: sudo mkfs.vfat /dev/sdb1
Langkah 6: Lakukan mount SSD:
Buat titik mount: sudo mkdir /mnt/myssd
Lakukan mount SSD: sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/myssd
Jangan lupa mengganti nama /dev/sdb1 dengan nama partisi SSD Anda.
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-15
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-18
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-04
Apakah ini membantu?
Jika SSD Anda memerlukan firmware baru, Anda akan menerima notifikasi saat menjalankan perangkat lunak Kingston SSD Manager, yang ada di sini: www.kingston.com/ssdmanager
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-11
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-13
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-12
Apakah ini membantu?
Jika hal tersebut tidak memungkinkan, atau jika sebelumnya Anda telah mengklonakan data lama Anda ke drive baru tersebut, pastikan bahwa drive baru tersebut muncul sebagai perangkat boot di BIOS sistem, lalu pilih drive tersebut untuk proses boot.
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-03
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-18
Apakah ini membantu?
Jika drive terlihat di BIOS, Anda mungkin perlu menginisialisasi disk dalam sistem operasi.
Untuk Windows:
Langkah 1: Pastikan bahwa drive telah dipasang dengan baik, lalu hidupkan sistem untuk melakukan boot ke Sistem Operasi Windows.
Langkah 2: Tekan tombol Windows + X, lalu pilih Manajemen Disk.
Langkah 3: Jika SSD masih baru dan belum diinisialisasi, jendela sembul akan muncul dengan pesan “Inisialisasi Disk”.
Langkah 4: Pilih antara:
MBR (Master Boot Record): Cocok untuk drive berkapasitas di bawah 2TB dan sistem operasi lama.
GPT (GUID Partition Table): Dianjurkan untuk sistem terbaru dan drive berkapasitas lebih dari 2TB.
Langkah 5: Klik OK untuk menginisialisasi disk.
Langkah 6: Setelah terinisialisasi, status SSD akan menjadi “Unallocated" (Tidak dialokasikan). Klik kanan pada disk, lalu pilih New Simple Volume (Volume Baru Biasa).
Langkah 7: Ikuti perintah di layar untuk memformat dan menetapkan huruf drive untuk SSD.
Untuk Mac OS:
Langkah 1: Pastikan drive terpasang dengan baik, hidupkan sistem, lalu boot ke Mac OS.
Langkah 2: Buka Utilitas Disk (dapat ditemukan dengan menggunakan Spotlight dengan tombol Cmd + spasi lalu mengetikkan “Disk Utility”).
Langkah 3: Di panel kiri, pilih SSD Anda.
Langkah 4: Klik Hapus.
Langkah 5: Berikan nama pada drive, lalu pada menu Format, pilih:
APFS untuk perangkat SSD dan Mac yang lebih baru.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled) untuk sistem atau HDD yang lebih lama.
Langkah 6: Klik Hapus. Setelah proses ini selesai, SSD akan siap digunakan.
Untuk Linux:
Langkah 1: Pastikan drive terpasang dengan baik, hidupkan sistem, lalu boot ke Linux OS.
Langkah 2: Buka terminal.
Langkah 3: Ketikkan perintah sudo fdisk -l untuk menampilkan semua drive yang terhubung. Identifikasikan SSD Anda dari ukurannya dan catat nama perangkatnya, mis., /dev/sdb.
Langkah 4: Lakukan inisialisasi SSD menggunakan perintah fdisk atau parted. Berikut panduan dasar penggunaan perintah fdisk:
Ketikkan perintah sudo fdisk /dev/sdb (ganti /dev/sdb dengan nama perangkat SSD Anda).
Tekan "g" untuk membuat tabel partisi GPT baru.
Tekan "n" untuk membuat partisi baru. Ikuti perintah untuk menentukan ukuran dan jenis.
Tekan "w" untuk mengonfirmasikan dan menyimpan perubahan ke disk.
Langkah 5: Format partisi baru pada SSD (mis., /dev/sdb1). Anda dapat memformatnya dengan menggunakan sistem file pilihan Anda:
Untuk ext4: sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
Untuk ext3: sudo mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
Untuk FAT32: sudo mkfs.vfat /dev/sdb1
Langkah 6: Lakukan mount SSD:
Buat titik mount: sudo mkdir /mnt/myssd
Lakukan mount SSD: sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/myssd
Jangan lupa mengganti nama /dev/sdb1 dengan nama partisi SSD Anda.
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-15
Apakah ini membantu?
FAQ: KSD-012010-001-14
Apakah ini membantu?
Still Need Assistance?
Hubungi Dukungan Teknis
Senin-Jumat 6 pagi-5 sore. PT
+1 (800)435-0640