Ask a Server SSD Expert
Planning the right solution requires an understanding of your project's storage goals. Let Kingston's experts guide you.
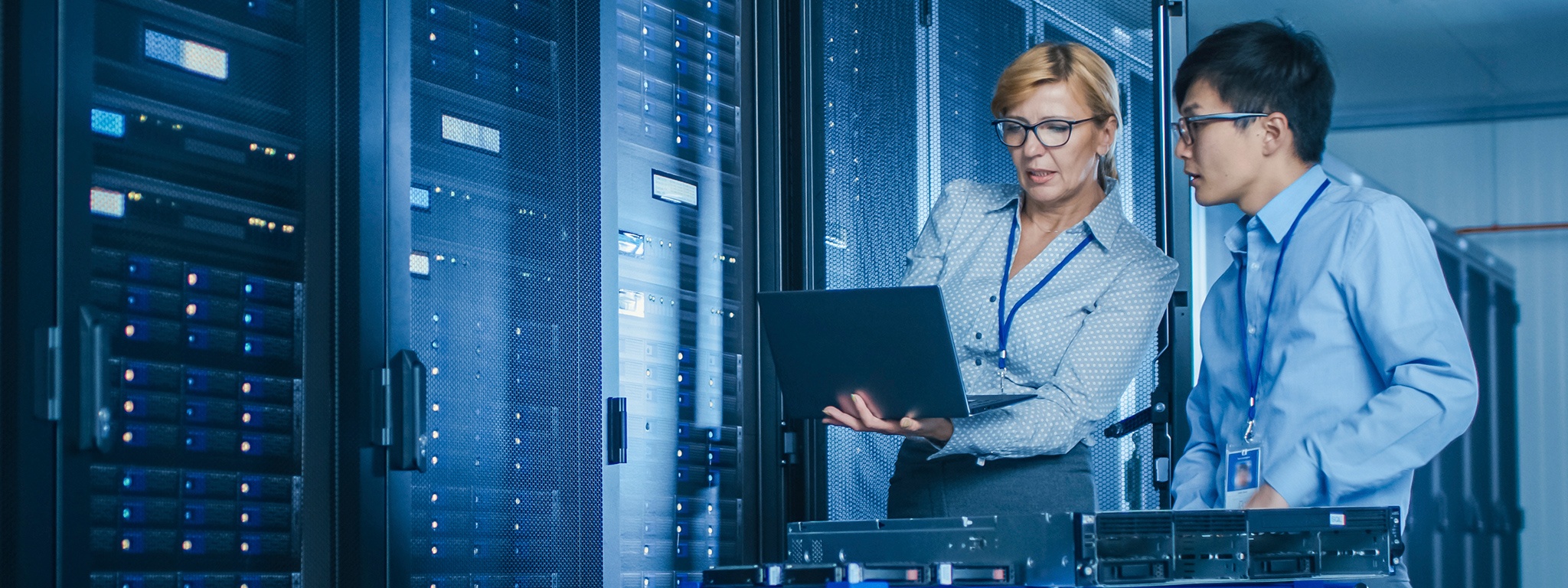


Data center SSDs (Solid State Drives) are specifically designed for use in data centers and enterprise-level applications, while client SSDs are designed for consumer-level applications. Here are five reasons why you should use data center SSDs rather than client SSDs in a server:
Data center SSDs are designed to handle a higher volume of read/write operations over their lifetime compared to client SSDs. This means they can withstand the demands of data center environments where there is a high workload and constant demand for data access.
Data center SSDs are built with components that are more robust and have a longer lifespan compared to client SSDs. They are designed to operate 24/7, and have additional features like power loss protection and data path protection that help prevent data loss.
Data center SSDs are optimized for high performance in data center environments. They offer IOPs consistency and predictable low latency (also known as Quality of Service) while servicing an intensive read/write workload. This means they can handle more I/O operations per second, making them ideal for applications that require high-speed data access.
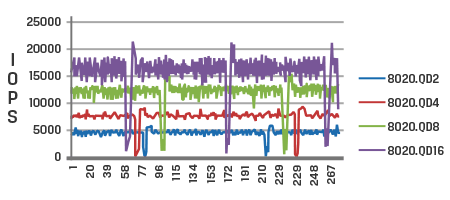
Time in seconds
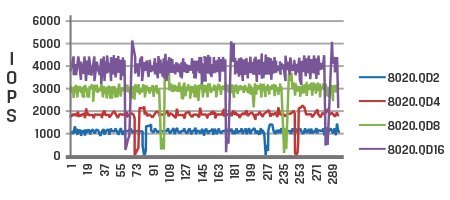
Time in seconds
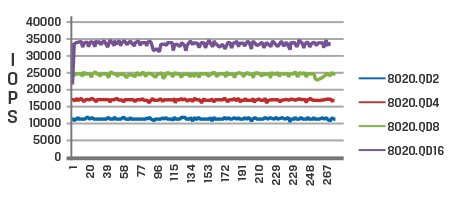
Time in seconds
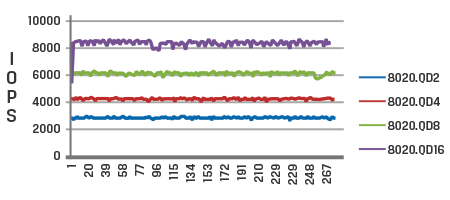
Time in seconds
The graphs display the difference in performance between a client SSD (top) and a data center SSD (bottom) when subjected to the same workloads.
The client SSD graph exhibits significant fluctuations in IOPS (Input/Output Operations per Second) with a high coefficient of variation, particularly under demanding workloads. This inconsistency is not desirable for data center customers, as it leads to inconsistent performance, resulting in slow response times when reading or writing data.
In contrast, the data center SSD graph demonstrates higher and more consistent IOPS compared to the client SSD. It exhibits a lower coefficient of variation, indicating stable performance and consistently low response times across various workloads.
Consistent IOPS and predictable low latency, also known as Quality of Service (QoS), are crucial factors considered for data-center-grade SSDs.
Data center SSDs have advanced features like end-to-end data protection that ensure data is protected at every stage of the data transfer process. They also have features like hardware encryption and secure erase, which help protect sensitive data.
Data center SSDs are tested on server platforms with third-party & OEM RAID controllers to guarantee their compatibility with this hardware.
Overall, using data center SSDs rather than client SSDs in a server can offer significant benefits in terms of higher endurance, better reliability, improved performance, advanced features, and better support. While client SSDs may be suitable for consumer-level applications, they are not designed to handle the demands of a data center environment.
You can find more information about our Kingston data center SSDs on our solutions page or you can Ask an Expert to help you choose the right SSD for your applications and workloads.
#KingstonIsWithYou

Planning the right solution requires an understanding of your project's storage goals. Let Kingston's experts guide you.

Simon Bestman explores SSD advantages over HDDs, storage trends, and future tech like PCIe Gen 5.

Simon Besteman explains the current and future challenges for data centers.