Ask a Server SSD Expert
Planning the right solution requires an understanding of your project’s security goals. Let Kingston’s experts guide you.
Your web browser is out of date. Update your browser now for better experience on this site. https://browser-update.org/update-browser.html


For those who manage server data storage, Drive Writes Per Day (DWPD) has emerged as a key metric, influencing the longevity and performance of solid-state drives (SSDs). As organizations increasingly rely on SSDs for faster data access and improved system responsiveness, understanding the significance of DWPD becomes paramount. This article aims to demystify DWPD and help you determine how much you really need.
What are Drive Writes Per Day (DWPD)? It's a measure of the endurance of an SSD, indicating the number of times the drive's entire capacity can be written to per day over its warranty period. Essentially, it quantifies the drive's ability to withstand data write operations without experiencing a failure. DWPD is a core factor in determining the suitability of an SSD for specific use cases or applications, particularly in enterprise environments where heavy read and write workloads are common.
To determine how many DWPD you really need, it's essential to assess the anticipated workload and data write patterns of your application or system. For most consumer and desktop/laptop use cases, such as gaming, content consumption, corporate use, and general computing, SSDs with lower DWPD ratings are typically sufficient.
However, for enterprise environments, especially those involving databases, virtualization, and content creation, higher DWPD values may be necessary vs. their consumer counterparts. This is why you should consider the following when calculating your DWPD requirements:
Workload characteristics:
Identify the nature of your data workload. Is it read-intensive, write-intensive, or a balanced mix of both? And analyze your application I/O patterns to understand the volume of write operations.
Application requirements:
Different applications have varying demands on storage. Database servers, for instance, often require higher DWPD due to frequent write operations.
Storage capacity:
Larger capacity SSDs generally have higher endurance levels and can offer further flexibility though RAID utilization. Evaluate your storage needs and choose drives that align with your capacity requirements.
Warranty period:
DWPD is calculated over the drive's warranty period. Consider the length of the warranty when assessing your requirements.
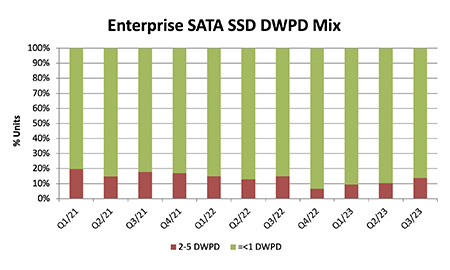
For enterprise SSDs, many look towards larger DWPD numbers without truly considering what they need. And in tougher economic times, understanding and buying what you need is key to ensuring you obtain the right balance between cost, performance, and longevity.
For many that are looking to purchase SATA-based SSDs—whether refreshing SSDs or transitioning away from HDDs—a key question is, do you need higher than 1 DWPD?
Maybe not. Evidence of this is a recent report from Forward Insights—revealing the current mix of enterprise SATA drives and DWPD. It suggests that the majority (82.3%) of data centers and enterprises that run SATA-based drives in their servers achieve success by using drives that are actually less than 1 DWPD.
Balancing performance, cost, and endurance is fundamental when selecting an SSD with an appropriate DWPD rating. While higher DWPD values offer greater endurance, they often come with a higher price premium. It's essential to strike a balance that meets your application's needs without overspending on what could be deemed unnecessary.
Additionally, advancements in SSD technology, such as wear leveling algorithms, contribute to extending the lifespan of SSDs. These features help distribute write and erase cycles evenly across the drive, minimizing the risk of premature wear.
An example of this is Kingston's DC600M SSD, which is a cutting-edge fourth-generation data center SATA 3.0, 6Gbps SSD—equipped with 3D TLC NAND, specifically designed for "mixed use" workloads. Tailored for deployment in high-volume rack-mount servers, the DC600M features on-board power loss protection (PLP) hardware through power loss capacitors, safeguarding data from unexpected power failures, minimizing the risk of data loss, and ensuring successful re-initialization upon the next system power-up.
Engineered to provide consistent latency and IOPS for system integrators, enterprises with on-premise servers, hyperscale data centers, and cloud service providers, the DC600M is available in capacities ranging from 480GB to 7680GB, offering a comprehensive range to meet diverse data storage requirements—and backed by a 5-year warranty.
Drive Writes Per Day (DWPD) is a key consideration when choosing an enterprise SSD that aligns with your data storage needs. By carefully assessing your application's workload, understanding I/O patterns, and considering other factors like capacity and warranty, you can determine the optimal DWPD rating for your specific use case.
Our Ask an Expert team is on hand to answer your questions and offer guidance on how you can achieve your goals. After all, getting the right balance ensures that your SSD not only performs reliably but also offers a cost-effective solution tailored to your requirements.
#KingstonIsWithYou
Was this helpful?

Planning the right solution requires an understanding of your project’s security goals. Let Kingston’s experts guide you.

Simon Bestman explores SSD advantages over HDDs, storage trends, and future tech like PCIe Gen 5.

Simon Besteman explains the current and future challenges for data centers.

Follow DASH Pictures' journey as they addressed slow HDD storage issues during media production, and how they worked with Kingston to adopt fast SSD storage to improve their on-location and post-production processes.

Is the world ready for 5G? While apps, devices, and more claim 5G-readiness, networks are scrambling. True 5G depends on edge computing: data being closer to customers.

In this video, we explain how Kingston and 2CRSi work together to solve data center challenges.

Some enterprises still make use of client SSDs to handle high-intensity server tasks, then rip & replace them when they fail to maintain the required standard of performance. Learn why that’s a false economy and how enterprise-level drives can increase organizational efficiency.

SSDs are all alike, right? You plug it in and instantly have all of that Flash Memory available for your workload? Right? If you answered yes, then you’ve probably fallen to one of the 4 biggest mistakes you could make when selecting your SSD.

Choosing the right SSD is important since not all SSDs are alike. When it comes to data centers, choosing an SSD with the right performance consistency with low latencies that’s specifically built for enterprise and data center workloads is key for consistent and reliable performance.
With the rise of data, need of edge computing and edge networks data center upgrades with NVMe SSDs enable more possibilities than before.

So you want to drastically improve the speed of your PC with an SSD upgrade. But how do you choose?

In this ChalkTalk Video, Storage Swiss's Lead Analyst George Crump and Kingston Technology’s Cameron Crandall talk SSD.
No products match your current filter selection. Try adjusting your filters to explore more options.

The differences between SSD classes lies in two components; the processor and the NAND memory.

Join Simon Bestman to explore SSD benefits over HDDs and the latest storage trends.

Reasons why a NAS would benefit your home or small office setup.

System Integrators in India grew their business and reputation using Kingston’s reliable products.

Here is a list of USB security features to consider for data protection.

Learn what the 3-2-1 data backup method is and why it is your best defense against ransomware.

Simon Besteman explains the current and future challenges for data centers.

Explore DRAM technology’s evolution and gain insights into future trends in our eBook.

Learn how Terabytes Written and Drive Writes Per Day are defined, and their differences.

We explore the different types of memory & how to make the right choice for your server.

Read the whitepaper to learn how DC600M helps vSAN demand performance and efficiency.

Kingston sets industry standards with unwavering commitment to quality and reliability.

Kingston and QNAP have improved the efficiency of digital theaters with their hardware.

Questions to ask when seeking the right SSD for your organization’s data center.

We explore the how media organizations can speed up workflows through storage and memory.

2023 has been a year full of challenges and innovations. But what will 2024 bring?

Elevate your data center with Kingston's VMware-compatible DC600M enterprise SSDs.

Kingston's server SSD and memory transformed Android Basha's production workflow.

Kingston storage solutions help improve performance photographer Ralph Larmann’s workflow.

DASH Pictures enhances their media production efficiency with Kingston SSDs.

Discover why upgrading your technology in this economy matters more than ever.

Server SSDs have higher endurance, better reliability, and improved performance over client SSDs.

We explore the benefits of upgrading vs. replacing, and how organizations can succeed.
Assess your existing server hardware to extend its lifespan and maximize your investment.

Learn about NVMe and why choosing it is beneficial to your organization’s infrastructure.

We discuss the journey of digital twin technology, exploring real-world examples for success.

In this whitepaper, we explain the benefits of SDS vs. its HW and SW RAID counterparts.

In this video, we explain how Kingston and 2CRSi work together to solve data center challenges.

Learn why APLIGO chose Kingston SSD and memory to support their system integration business.

Choosing storage products for your enterprise is a complex process. Kingston offers our expertise.

Learn how Kingston and QNAP solutions help optimize content creation.

Learn how Kingston supported a leading hosting provider with optimal configuration.

Kingston examines how its DC1500M Enterprise NVMe SSD affects workloads and compares to competitors.

In this eBook, we speak with experts about the journey of data storage, and what the future holds.

From shooting, to post-production, to encoding, to distribution at data centres, SSDs and RAM are powering the world of OTT Media & Entertainment (M&E) video and audio streaming.

We explore the top 12 tips small and medium size enterprises can take to enhance cybersecurity.

This infographic is about the different types of data centers, the myths, and Kingston's DC solutions.

We’ve examined several factors using unique research to identify what may impact markets globally in 2022.

2021 has been a year full of challenges and innovations. But what will 2022 bring?

Read our eBook, about the rise of digital transformation and what the future holds.

Bill Mew shares his thoughts how the largest security challenges need commitment from the boardroom.

Rob May shares his thoughts on how close we are to edge computing and the security it requires.

The high-performance DC500M Server SSD is the best storage choice for a pro videographer.

Memory and storage have evolved over the years. Get an insight from our industry expert.

Our partnership with Microchip’s RAID controllers helps deliver high performance for server storage.

Kingston helped optimize Simply Hosting’s storage in its data centers to ensure they were always on.

Learn how Kingston helped to lower power costs and increase performance so Hostmein could deliver on SLAs.

In this eBook, we speak with experts about IoT’s journey and prepare organizations for IoT’s future.

The pandemic has increased internet traffic which has placed importance on the role of data centers.

Cameron Crandall of Kingston helps you self-evaluate the need to move to your server storage solution to NVMe.

NVMe over Fabric helps CPUs to run more efficiently with lower latency and higher throughput.

Join industry experts to discuss how technology partners like Kingston support their business growth and sustainability.

Industry experts discuss topics like the key pillars of tech relationships, sustainability, and IT optimization.
Watch this webinar to discover the benefits of NVMe SSDs.

The switch to NVMe requires a full stack review from IT architects to ensure redundancy exists on every layer of the stack.

In this eBook, we talk to industry experts as we explore the benefits of artificial intelligence, how it’s fuelling data consumption and how you can prepare your organization for the opportunities it presents.

Here are seven of the predictions of what will drive NVMe adoption for 2021.

Test SSDs to know the real endurance, changes in latency and IOPS in sequential and random read or write scenarios.

SSD test beds for enterprise servers should be done with the real hardware, OS and data. We’ll explain why.

MSP industry expert Rob May’s insight into how memory/storage upgrades help companies with remote workers.

Don’t pick the wrong type of SSD for your server. A wrong choice means a higher cost of ownership. Learn to pick the right SSDs.

What will 2021 bring in tech and trends? What do our KingstonCognate members and industry experts predict for the future?

Learn why the future of business depends on SSD-enabled SDS, and how SSD fits into software-defined storage solutions.

Planning a new system? Watch this video to learn about the benefits 16Gbit DRAM next-gen technology.

Learn how Hosteur supported their rapid growth & SLAs with Kingston Enterprise products & services.

Data centers should be using server SSDs. There are many benefits over client drives and costs have come down.

NVMe is now the standard protocol for SSDs to empower data centers and enterprise environments.

Find out how Hardwareluxx were able to manage the growth of their web traffic using Kingston's DC500M SSD.

SDS hasn’t lived up to its hype but now that NVMe is more affordable the commodity hardware is ready to deliver.

Choosing the right SSD for your server is important since server SSDs are optimized to perform at a predictable latency level while client (desktop/laptop) SSDs are not. These difference result in better uptime and less lag for critical apps and services.

Industry expert Simon Besteman provide insight on why 5G demands edge computing in micro data centers.

Cloud and on-premise data center managers can learn a lot from supercomputing.

What are the demands of the Data Centers in these unprecedented times? Read this article from Industry Expert, Dr Sally Eaves & she will provide you with an insight on the demands.

Kingston delivered compatible memory that met the performance goals of i3D.net's servers, extending the service life of their existing hardware.

Why is Edge Computing Data Centers important for 5G? Download and read Kingston’s eBook on Edge Servers and the 5G rollout.

This whitepaper demonstrates how using Kingston Technology’s Data Centre DC500 SSDs can reduce your overall capital and licence costs by 39%.

Data Center 500 Series SSDs (DC500R / DC500M) – Consistency, predictability of Latency (response time) and IOPS (I/Os Per Second) performance.

End-to-End Data Protection protects customer’s data as soon as it is transferred by the host system to the SSD, and then from the SSD to the host computer. All Kingston SSDs incorporate this protection.

SDS provides a policy-based control of data tiers, independent of the underlying storage hardware.

A percentage of space on an SSD is reserved for OP in firmware. OP can improve performance.

Firmware/hardware PFAIL protection is an highly effective method for preventing data loss in enterprise SSD.
Kingston uses LSI® SandForce®-based controllers in some SSDs that use proprietary tech for Garbage Collection.

HPC can require massive amounts of data. SSDs consume a fraction of the power of their spinning disk.

Kingston datacenter SSDs provide excellent resiliency to protect sensitive data in OLTP workloads.

Frequently asked questions around SSD technologies and terms like SATA, M.2, NAND, RAID, NVMe, PCIe, SAS, and keying.

Storage can be the most challenging component for VDI performance.

Testing is a cornerstone of our commitment to deliver the most reliable products on the market. We perform rigorous tests on all of our products during each stage of production. These tests ensure quality control throughout the entire manufacturing process.

Learn how DDR4 delivers faster speeds, reduced power consumption and increased capacity over DDR3.


