32Gbit density planar (non-stacked) DDR5 DRAM production began in the second half of 2024 from the world’s leading DRAM semiconductors, enabling new, high capacity DDR5 modules for client and server-class systems. Using advanced next-generation lithography, 32Gbit DRAM packs more memory cells into the same physical package size as 16Gbit and 24Gbit DDR5 chips. More cells per chip mean more capacity for existing memory module form factors, such as DIMMs and SODIMMs, allowing systems to achieve higher total capacities not seen before without using costly stacked DRAM (3D TSV / DDP) technologies.
UDIMM/CUDIMM/SODIMM/CSODIMM with 32Gbit DRAM
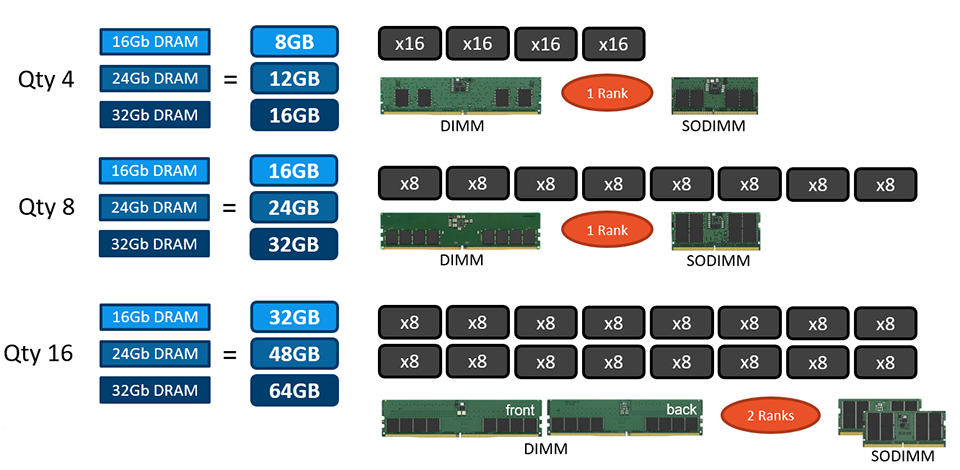
4x (2G x16) DRAM = 16GB in 1 Rank
8x (4G x8) DRAM = 32GB in 1 Rank
16x (4G x8) DRAM = 64GB in 2 Ranks
Traditional desktop systems with a four-socket dual channel memory architecture can achieve up to 256GB with 64GB UDIMMs/CUDIMMs, while laptops and small form factor systems using the SODIMM/CSODIMM form factor can achieve a total 128GB of system RAM in two sockets.
Servers and workstations primarily benefit from the cost savings and unrestricted availability of 128GB capacity Registered DIMMs (RDIMMs) using 32Gbit DRAM, since this and higher capacity DDR5 RDIMMs were previously restricted to using 3DS stacked DRAM components.
Module Configurations (Non-ECC Unbuffered)
RDIMM with 32Gbit DRAM
10x (4G x8) DRAM = 32GB in 1 Rank
20x (4G x8) DRAM = 64GB in 2 Ranks
20x (8G x4) DRAM = 64GB in 1 Rank
40x (8G x4) DRAM = 128GB in 2 Ranks
Module Configurations (ECC Registered)

Select Intel and AMD DDR5 server and client platforms support 32Gbit DRAM. BIOS updates may be required to enable support on some legacy systems, so be sure to check with the system or motherboard manufacturer for the latest firmware.
| 32Gbit | ||
| PC/LAPTOP | Intel Ultra Series 2 / 800-Series Chipset | YES |
| Intel 14th Gen / 700-Series Chipset | SELECT BOARDS WITH BIOS UPDATE |
|
| Intel 13th Gen / 700-Series Chipset | SELECT BOARDS WITH BIOS UPDATE |
|
| Intel 12th Gen / 600-Series Chipset | NO | |
| AMD Ryzen (AM5) / 800-Series Chipset | SELECT BOARDS WITH BIOS UPDATE |
|
| AMD Ryzen (AM5) / 600-Series Chipset | SELECT BOARDS WITH BIOS UPDATE |
|
| SERVER/WORKSTATIONS |
Intel Xeon 6 (Granite Rapids-SP/AP only) | YES* |
| Intel 5th Gen Xeon SP | NO | |
| Intel 4th Gen Xeon SP | NO | |
| Intel W 3500/2500 Series / W790 Chipset Intel W 3400/2400 Series / W790 Chipset |
NO | |
| AMD 5th Gen EPYC | YES | |
| AMD 4th Gen EPYC | NO | |
| AMD Ryzen Threadripper/PRO 7000 Series / WRX90/TRX50 Chipsets | NO | |
* Only specific capacities and configurations
Kingston was the first memory module manufacturer to build 64GB UDIMMs featuring 32Gbit DRAM for demonstration at CES 2024, and worked closely with major motherboard manufacturers (ASRock, Gigabyte, MSI) in late 2023 to enable them to achieve 256GB total memory capacity on their systems.
High-capacity modules built with 32Gbit density are now available from Kingston. Use our on-line Configurator to verify compatibility with your specific make and model system.