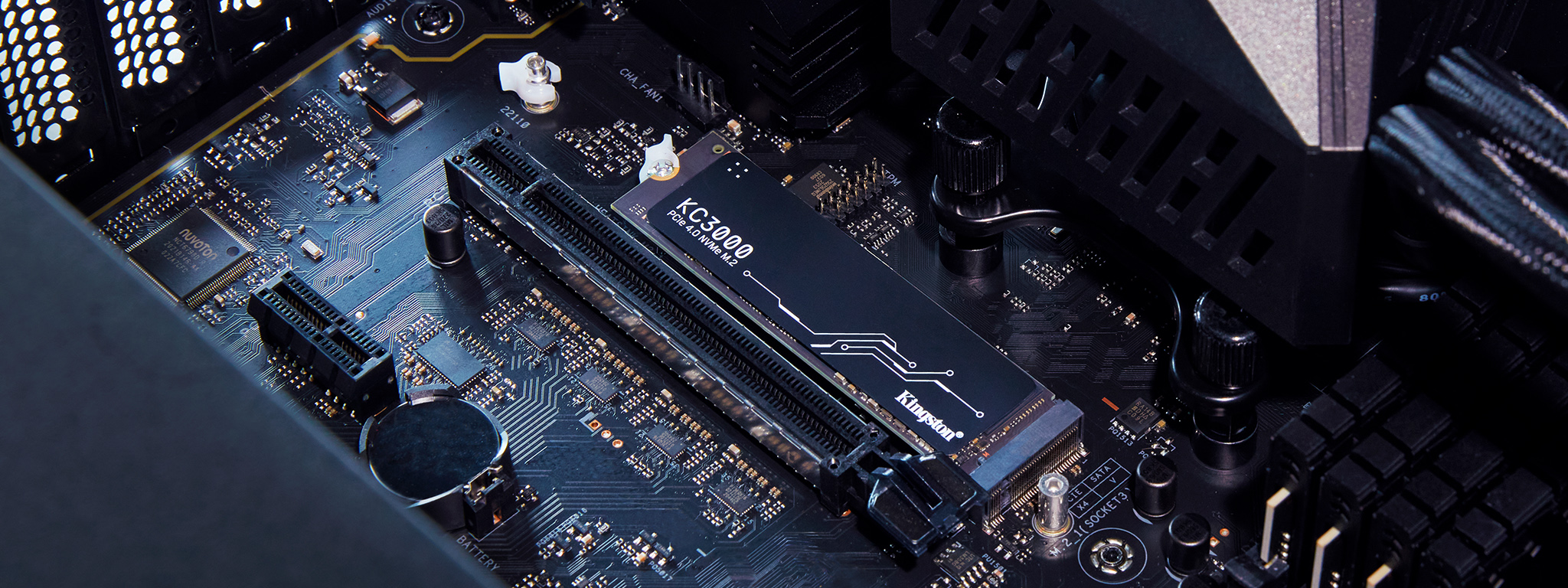
PCIe has been the standard interface for connecting high-speed peripheral components to computer motherboards for the past decade. The fourth generation of this interface, PCIe 4.0 standard, was announced in 2017. However, we did not see SSDs or graphics cards using the new tech until Computex 2019. Today, PCIe 4.0 has attracted an upsurge of excitement for this technological innovation whether it be SSDs, GPUs, motherboards or high-powered expansion cards. But what is PCIe Gen 4? We’ll break down the basics.

What is PCIe Gen 4?
PCIe Gen 4 is the fourth and latest generation of the PCI Express specification. The successor to PCIe Gen 3, PCIe Gen 4 is the fastest PCIe generation available on the market today.
What does PCIe Gen 4 do?
PCIe Gen 4 allows systems to connect to high-performance PCIe devices such as GPUs and PCIe NVMe SSDs.
Why is PCIe Gen 4 necessary?
Advancement in PCIe technology is necessary to accommodate the growing need for a high-speed data bus that enables increasingly demanding user applications and workloads.